Desarrollo experimental de controladores Fuzzy para procesos térmicos y neumáticos
Main Article Content
Keywords
Raspberry PI, sistema de control, Instrumentación, Fuzzy, Python
Resumen
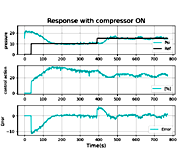
En este proyecto, se propone un sistema de control Fuzzy en un módulo de entrenamiento de procesos industriales con dos sistemas independientes entre sí, uno térmico y otro neumático, el algoritmo de control se desarrolla en lenguaje Python v3.6 ejecutado por una Raspberry Pi B+, ambos controladores dependen del error y cambio en el error que se actualizan en tiempos de 2 s y 1 s, para temperatura y presión respectivamente, la comunicación con las plantas emplea conversores A/D y D/A, el Fuzzy térmico se analizo con tres referencias de temperatura [50,100 y 150]°C, con un tiempo de subida de 191 s, 360 s y 505 s; error de estado estacionario de 5.5 %, 0.7% y 0.7 %, en el sistema neumático se evalúo la velocidad de cambio entre referencias de 10 psi a 15 psi variando la activación del compresor al inicio de los experimentos, los tiempos de asentamiento que se obtienen son 111 s y 106 s, con el compresor apagado el resultado es de 116 s y 88 s, además de un sobrepaso máximo de 13% con oscilaciones inherentes al tipo sistema que se encuentran en un rango aceptable.
Descargas
Referencias
[2] H. J. Ferreau, S. Almér, R. Verschueren, M. Diehl, D. Frick, A. Domahidi, J. L. Jerez, G. Stathopoulos, and C. Jones, “Embedded optimization methods for industrial automatic control,” IFAC-PapersOnLine, vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 13 194–13 209, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2017.08.1946.
[3] F. Ponci, A. Sadu, R. Uhl, M. Mirz, A. Angioni, and A. Monti, “Instrumentation and measurement testing in the real-time lab for automation of complex power systems,” IEEE Instrumentation & Measurement Magazine, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 17–24, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1109/MIM.2018.8278805.
[4] E. Harper, Elementos del control de procesos. Limusa noriega editores, 2015, ch. 1, pp. 11–51.
[5] J. Huo, F. T. Chan, C. K. Lee, J. O. Strandhagen, and B. Niu, “Smart control of the assembly process with a fuzzy control system in the context of industry 4.0,” Advanced Engineering Informatics, vol. 43, p. 101031, 2020.
[6] J. L. Riviello, E. L. Riviello, J. H. Reyes, and C. G. Escarpeta, “Implementation of fuzzy controller in different embedded systems,” in 2019 IEEE International Conference on Engineering Veracruz (ICEV), vol. 1. IEEE, 2019, pp. 1–4, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEV.2019.8920584.
[7] R. P. FOUNDATION. (2015) Raspberry pi 2 model b. https://www. raspberrypi.org/products/raspberry-pi-2-model-b/
[8] J. Li, Q. Xiong, K. Wang, X. Shi, and S. Liang, “A recurrent self-evolving fuzzy neural network predictive control for microwave drying process,” Drying Technology, vol. 34, no. 12, pp. 1434–1444, 2016, https://doi.org/10.1080/07373937.2015. 1122612.
[9] J. M. Celis-Peñaranda, C. D. Escobar-Amado, S. B. Sepúlveda-Mora, S. A. Castro-Casadiego, B. Medina-Delgado, and J. J. Ramírez-Mateus, “Control adaptativo para optimizar una intersección semafórica basado en un sistema embebido,” Ingeniería y ciencia, vol. 12, no. 24, pp. 169–193, 2016, https://doi.org/10. 17230/ingciencia.12.24.8.
[10] P. Navdeti, S. Parte, P. Talashilkar, J. Patil, and V. Khairnar, “Patient parameter monitoring system using raspberry pi,” International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science, vol. 5, no. 3, 2016, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCTIDE. 2016.7725378.
[11] G. Macias-Bobadilla, J. Becerra-Ruiz, A. A. Estévez-Bén, and J. Rodríguez- Reséndiz, “Fuzzy control-based system feed-back by obd-ii data acquisition for complementary injection of hydrogen into internal combustion engines,” International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020. 07.084.
[12] J. R. García-Martínez, E. E. Cruz-Miguel, R. V. Carrillo-Serrano, F. Mendoza-Mondragón, M. Toledano-Ayala, and J. Rodríguez-Reséndiz, “A pid-type fuzzy logic controller-based approach for motion control applications,” Sensors, vol. 20, no. 18, p. 5323, 2020, https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185323. 99
[13] U. Zalabarria, E. Irigoyen, R. Martinez, M. Larrea, and A. Salazar-Ramirez, “A low-cost, portable solution for stress and relaxation estimation based on a real-time fuzzy algorithm,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 74 118–74 128, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2988348.
[14] H. Fakhrurroja, S. A. Mardhotillah, O. Mahendra, A. Munandar, M. I. Rizqyawan, and R. P. Pratama, “Automatic ph and humidity control system for hydroponics using fuzzy logic,” in 2019 International Conference on Computer, Control, Informatics and its Applications (IC3INA). IEEE, 2019, pp. 156–161, https://doi.org/10.1109/IC3INA48034.2019.8949590.
[15] M. J. Villaseñor-Aguilar, J. E. Botello-Álvarez, F. J. Pérez-Pinal, M. Cano- Lara, M. F. León-Galván, M.-G. Bravo-Sánchez, and A. I. Barranco- Gutierrez, “Fuzzy classification of the maturity of the tomato using a vision system,” Journal of Sensors, vol. 2019, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3175848.
[16] M. Das, V. Sivakami, A. Pal, and B. Vasuki, “Analog-digital conditioning circuit for rtd temperature measurement,” in 2018 15th IEEE India Council International Conference (INDICON). IEEE, 2018, pp. 1–5, https://doi.org/10.1109/ INDICON45594.2018.8987077
[17] A. Rai and D. Yadav, “Evaluating wiring configurations for rtd sensor in temperature measurement,” I-Manager’s Journal on Electronics Engineering, vol. 10, no. 1, p. 1, 2019, https://doi.org/10.26634/jele.10.1.16422.
[18] RTD-to-Digital Converter, maxim integrated, 07 2015, rev. 3.
[19] Transmisor de presión para aplicaciones generales industriales. Tipo MBS 3000 y MBS 3050, Danfoss, 09 2013.
[20] F. Kurokawa and S. Hattori, “Single stage ad-dc full-bridge converter for battery charger,” in 2015 IEEE International Telecommunications Energy Conference (INTELEC). IEEE, 2015, pp. 1–6, https://doi.org/10.1109/INTLEC.2015. 7572402.
[21] R. Skrbina and D. Team, “Filtered pwm digital to analog converter,” Design team, vol. 10, no. 4, 2015.
[22] E. A. W. Hung T. Nguyen, Carol L. Walker, FUZZY MODELING AND CONTROL. CRC Press, 2018, ch. 13, pp. 385–399.
[23] H.-R. Lin, B.-Y. Cao, and Y.-z. Liao, “Fuzzy control,” in Fuzzy Sets Theory Preliminary. Springer, 2018, pp. 73–108, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-70749-5_3.
[24] G. Yang, J.-M. Du, X.-Y. Fu, and B.-R. Li, “Asymmetric fuzzy control of a positive and negative pneumatic pressure servo system,” Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, vol. 30, no. 6, pp. 1438–1446, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1007/ s10033-017-0194-1.
[25] C.Wang, “A study of membership functions on mamdani-type fuzzy inference system for industrial decision-making,” 2015.
[26] O. A. M. Ali, A. Y. Ali, and B. S. Sumait, “Comparison between the effects of different types of membership functions on fuzzy logic controller performance,” International Journal, vol. 76, pp. 76–83, 2015, Corpus ID:736797.
[27] Y.-J. Wang, “Ranking triangle and trapezoidal fuzzy numbers based on the relative preference relation,” Applied mathematical modelling, vol. 39, no. 2, pp. 586–599, 2015, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2014.06.011.
[28] S. B. Zdenko Kovaˆcic, Fuzzy Controller Design. CRC Press, 2006, ch. 2, pp. 9–70.
[29] D. K. Sambariya and R. Prasad, “Selection of membership functions based on fuzzy rules to design an efficient power system stabilizer,” International Journal of Fuzzy Systems, vol. 19, no. 3, pp. 813–828, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1007/ s40815-016-0197-6
[30] D. Vyas, Y. Misra, and H. Kamath, “Comparison and analysis of defuzzification methods of a fuzzy controller to maintain the cane level during cane juice extraction,” in 2015 International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication Engineering Systems. IEEE, 2015, pp. 102–106, https://doi.org/10.1109/SPACES.2015.7058225.
[31] J. Warner, J. Sexauer, scikit fuzzy, twmeggs, alexsavio, A. Unnikrishnan, G. Castelão, F. A. Pontes, T. Uelwer, pd2f, laurazh, F. Batista, alexbuy, W. V. den Broeck, W. Song, T. G. Badger, R. A. M. Pérez, J. F. Power, H. Mishra, G. O. Trullols, A. Hörteborn, and 99991, “scikit-fuzzy/scikitfuzzy: Scikit-fuzzy 0.4.2,” Nov. 2019, https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3541384.
[32] S. Agapiou, O. Papaspiliopoulos, D. Sanz-Alonso, A. Stuart et al., “Importance sampling: Intrinsic dimension and computational cost,” Statistical Science, vol. 32, no. 3, pp. 405–431, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1214/17-STS611.
[33] D. Kim, J. Cai, K. B. Ariyur, and J. E. Braun, “System identification for building thermal systems under the presence of unmeasured disturbances in closed loop operation: Lumped disturbance modeling approach,” Building and Environment, vol. 107, pp. 169–180, 2016, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2016. 07.007.
[34] D. S. Bhandare and N. Kulkarni, “Performances evaluation and comparison of pid controller and fuzzy logic controller for process liquid level control,” in 2015 15th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS). IEEE, 2015, pp. 1347–1352, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCAS.2015.7364848