Una Guía para el estudio de nanopartículas magnéticas de óxidos de hierro con aplicaciones biomédicas. Parte II
Main Article Content
Keywords
Disipación de calor, hipertermia magnética, nanopartículas magnéticas, óxidos de hierro, cáncer
Resumen
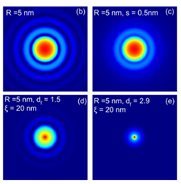
En esta segunda parte del artículo, se abordará el tema de la caracterización de nanopartículas magnéticas, haciendo énfasis en la interpretación de estas propiedades para definir la aplicación biomédica de los nanosistemas en estudio. Para el caso de nanopartículas de óxidos de hierro, se analizará como estas propiedades influyen en la disipación de calor de las nanopartículas cuando son sometidas a campos de radiofrecuencia, respuesta útil en el tratamiento del cáncer por hipertermia magética. En la hipertermia magnética, las partículas absorben energía de un campo de radio frecuencia
y la disipan en forma de calor, los rangos de frecuencia típicamente usados para pruebas in-vivo y en humanos están entre 50 y 1000 kHz y amplitudes entre 5 y 50 kA/m. Las propiedades de interés como magnetización, interacciones entre partículas y su ordenamiento, se estudian a partir de simulaciones computacionales y datos experimentales utilizando modelos de análisis adecuados para cada caso, ya planteados en la primera parte de este artículo. Finalmente se hace una correlación de estas propiedades con la disipación de calor, determinada por métodos calorimétricos, la cual se considera como parámetro de mérito para cuantificar la transducción de energía electromagnética a térmica.
Descargas
Referencias
[2] Z. Nemati, S. Salili, J. Alonso, A. Ataie, R. Das, M. Phan, and H. Srikanth, “Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanodiscs for hyperthermia therapy: Does size matter?” Journal of Alloys and Compounds, vol. 714, pp. 709 – 714, 2017. [Online]. Available: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/ S0925838817314068
[3] A. Sood, V. Arora, J. Shah, R. Kotnala, and T. K. Jain, “Multifunctional gold coated iron oxide core-shell nanoparticles stabilized using thiolated sodium alginate for biomedical applications,” Materials Science and Engineering: C, vol. 80, pp. 274 – 281, 2017. [Online]. Available: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0928493116324067
[4] J.-Q. Tang, X.-Y. Hou, C.-S. Yang, Y.-X. Li, Y. Xin, W.-W. Guo, Z.-P. Wei, Y.-Q. Liu, and G. Jiang, “Recent developments in nanomedicine for melanoma treatment,” International Journal of Cancer, vol. 141, no. 4, pp. 646–653, 2017. [Online]. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijc.30708
[5] C. Strehl, L. Maurizi, T. Gaber, P. Hoff, T. Broschard, A. R. Poole, H. Hofmann, and F. Buttgereit, “Modification of the surface of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles to enable their safe application in humans,” International Journal of Nanomedicine, vol. 11, pp. 5883–5896, 2016. [Online]. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S110579
[6] A. K. Silva, A. Nicolas-Boluda, L. Fouassier, and F. Gazeau, “Overcoming the tumor microenvironment: the role of nanohyperthermia,” Nanomedicine, vol. 12, no. 11, pp. 1213–1215, 2017. [Online]. Available: https: //doi.org/10.2217/nnm-2017-0096
[7] S. Sun, H. Zeng, D. B. Robinson, S. Raoux, P. M. Rice, S. X. Wang, and G. Li, “Monodisperse mfe2o4 (m = fe, co, mn) nanoparticles,” Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 126, no. 1, pp. 273–279, 2004, pMID: 14709092. [Online]. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja0380852
[8] A. G. Roca, M. P. Morales, K. O’Grady, and C. J. Serna, “Structural and magnetic properties of uniform magnetite nanoparticles prepared by high temperature decomposition of organic precursors,” Nanotechnology, vol. 17, no. 11, p. 2783, 2006. [Online]. Available: http://stacks.iop.org/0957-4484/ 17/i=11/a=010
[9] T. Yang, C. Shen, Z. Li, H. Zhang, C. Xiao, S. Chen, Z. Xu, D. Shi, J. Li, and H. Gao, “Highly ordered self-assembly with large area of fe3o4 nanoparticles and the magnetic properties,” The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, vol. 109, no. 49, pp. 23233–23236, 2005, pMID: 16375287. [Online]. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jp054291f
[10] T. Hyeon, S. S. Lee, J. Park, Y. Chung, and H. B. Na, “Synthesis of highly crystalline and monodisperse maghemite nanocrystallites without a size-selection process,” Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 123, no. 51, pp. 12798–12801, 2001, pMID: 11749537. [Online]. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja016812s
[11] P. Tartaj, M. del Puerto Morales, S. Veintemillas-Verdaguer, T. GonzálezCarreño, and C. J. Serna, “The preparation of magnetic nanoparticles for applications in biomedicine,” Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, vol. 36, no. 13, p. R182, 2003. [Online]. Available: http://stacks.iop.org/0022-3727/ 36/i=13/a=202
[12] N. R. Jana, Y. Chen, and X. Peng, “Size- and shape-controlled magnetic (cr, mn, fe, co, ni) oxide nanocrystals via a simple and general approach,” Chemistry of Materials, vol. 16, no. 20, pp. 3931–3935, 2004. [Online]. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/cm049221k
[13] P. D. Cozzoli, E. Snoeck, M. A. Garcia, C. Giannini, A. Guagliardi, A. Cervellino, F. Gozzo, A. Hernando, K. Achterhold, N. Ciobanu, F. G. Parak, R. Cingolani, and L. Manna, “Colloidal synthesis and characterization of tetrapod-shaped magnetic nanocrystals,” Nano Letters, vol. 6, no. 9, pp. 1966–1972, 2006. [Online]. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nl061112c
[14] C. B. Murray, S. Sun, W. Gaschler, H. Doyle, T. A. Betley, and C. R. Kagan, “Colloidal synthesis of nanocrystals and nanocrystal superlattices,” IBM Journal of Research and Development, vol. 45, no. 1, pp. 47–56, Jan 2001.
[15] J. Cheon, N.-J. Kang, S.-M. Lee, J.-H. Lee, J.-H. Yoon, and S. J. Oh, “Shape evolution of single-crystalline iron oxide nanocrystals,” Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 126, no. 7, pp. 1950–1951, 2004, pMID: 14971924. [Online]. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja038722o
[16] D. K. Yi, S. T. Selvan, S. S. Lee, G. C. Papaefthymiou, D. Kundaliya, and J. Y. Ying, “Silica-coated nanocomposites of magnetic nanoparticles and quantum dots,” Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 127, no. 14, pp. 4990–4991, 2005, pMID: 15810812. [Online]. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja0428863
[17] T. Pellegrino, L. Manna, S. Kudera, T. Liedl, D. Koktysh, A. L. Rogach, S. Keller, J. Rädler, G. Natile, and W. J. Parak, “Hydrophobic nanocrystals coated with an amphiphilic polymer shell: A general route to water soluble nanocrystals,” Nano Letters, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 703–707, 2004. [Online]. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nl035172j
[18] B. BITTOVA, J. P. VEJPRAVOVA, M. P. DEL MORALES, A. G. ROCA, D. NIZNANSKY, and A. MANTLIKOVA, “Influence of aggregate coating on relaxations in the systems of iron oxide nanoparticles,” Nano, vol. 07, no. 01, p. 1250004, 2012. [Online]. Available: http: //www.worldscientific.com/doi/abs/10.1142/S179329201250004X
[19] I. Nedkov, T. Merodiiska, L. Slavov, R. Vandenberghe, Y. Kusano, and J. Takada, “Surface oxidation, size and shape of nano-sized magnetite obtained by co-precipitation,” Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, vol. 300, no. 2, pp. 358 – 367, 2006. [Online]. Available: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304885305005433
[20] K. Tao, H. Dou, and K. Sun, “Interfacial coprecipitation to prepare magnetite nanoparticles: Concentration and temperature dependence,” Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, vol. 320, no. 1-3, pp. 115 – 122, 2008. [Online]. Available: http: //www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0927775708000721
[21] T. J. Daou, G. Pourroy, S. Bégin-Colin, J. M. Grenèche, C. Ulhaq-Bouillet, P. Legaré, P. Bernhardt, C. Leuvrey, and G. Rogez, “Hydrothermal synthesis of monodisperse magnetite nanoparticles,” Chemistry of Materials, vol. 18, no. 18, pp. 4399–4404, 2006. [Online]. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ cm060805r
[22] D. Kim, S. Lee, K. Im, K. Kim, K. Kim, I. Shim, M. Lee, and Y.-K. Lee, “Surface-modified magnetite nanoparticles for hyperthermia: Preparation, characterization, and cytotoxicity studies,” Current Applied Physics, vol. 6, Supplement 1, pp. e242 – e246, 2006, nano Korea 2005 Symposium Nano Korea 2005 Symposium. [Online]. Available: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1567173906000496
[23] R. Massart, “Preparation of aqueous magnetic liquids in alkaline and acidic media,” IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 17, no. 2, pp. 1247–1248, Mar 1981.
[24] S. Laurent, D. Forge, M. Port, A. Roch, C. Robic, L. Vander Elst, and R. N. Muller, “Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications,” Chemical Reviews, vol. 108, no. 6, pp. 2064–2110, 2008, pMID: 18543879. [Online]. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/cr068445e
[25] D. C. Lee, D. K. Smith, A. T. Heitsch, and B. A. Korgel, “Colloidal magnetic nanocrystals: synthesis, properties and applications,” Annu. Rep. Prog. Chem., Sect. C: Phys. Chem., vol. 103, pp. 351–402, 2007. [Online]. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/B605630J
[26] M.E.Fleet,“Thestructureofmagnetite:Symmetryofcubicspinels,” Journal of Solid State Chemistry, vol. 62, no. 1, pp. 75 – 82, 1986. [Online]. Available: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0022459686902185
[27] A. Jain, S. P. Ong, G. Hautier, W. Chen, W. D. Richards, S. Dacek, S. Cholia, D. Gunter, D. Skinner, G. Ceder, and K. a. Persson, “The Materials Project: A materials genome approach to accelerating materials innovation,” APLMaterials,vol.1,no.1,p.011002,2013.[Online].Available: http://link.aip.org/link/AMPADS/v1/i1/p011002/s1&Agg=doi
[28] G. F. Goya, T. S. Berquó, F. C. Fonseca, and M. P. Morales, “Static and dynamic magnetic properties of spherical magnetite nanoparticles,” Journal of Applied Physics, vol. 94, no. 5, pp. 3520–3528, 2003. [Online]. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1599959
[29] M. Khalkhali, K. Rostamizadeh, S. Sadighian, F. Khoeini, M. Naghibi, and M. Hamidi, “The impact of polymer coatings on magnetite nanoparticles performance as mri contrast agents: a comparative study,” DARU Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, vol. 23, no. 1, p. 45, 2015. [Online]. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s40199-015-0124-7
[30] K. Persson, “Materials data on fe3o4 (sg:227) by materials project,” Jan 2015. [Online]. Available: http://www.osti.gov/dataexplorer/servlets/purl/ 1194194
[31] G. K. Rozenberg, Y. Amiel, W. M. Xu, M. P. Pasternak, R. Jeanloz, M. Hanfland, and R. D. Taylor, “Structural characterization of temperatureand pressure-induced inverse↔normal spinel transformation in magnetite,”Phys. Rev. B, vol. 75, p. 020102, Jan 2007. [Online]. Available: http://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevB.75.020102
[32] F. Walz, “The verwey transition - a topical review,” Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, vol. 14, no. 12, p. R285, 2002. [Online]. Available: http://stacks.iop.org/0953-8984/14/i=12/a=203
[33] S. Sun and H. Zeng, “Size-controlled synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles,” Journal of the American Chemical Society, vol. 124, no. 28, pp. 8204–8205, 2002, pMID: 12105897. [Online]. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ ja026501x
[34] D. W. SCHAEFER, “Polymers, fractals, and ceramic materials,” Science, vol. 243, no. 4894, pp. 1023–1027, 1989. [Online]. Available: http: //science.sciencemag.org/content/243/4894/1023
[35] E. S. Gonçalves, D. R. Cornejo, C. L. P. Oliveira, A. M. Figueiredo Neto, J. Depeyrot, F. A. Tourinho, and R. Aquino, “Magnetic and structural study of electric double-layered ferrofluid with mnfe2o4@γ−fe2o3 nanoparticles of different mean diameters: Determination of the magnetic correlation distance,” Phys. Rev. E, vol. 91, p. 042317, Apr 2015. [Online]. Available: http://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevE.91.042317
[36] T. Freltoft, J. K. Kjems, and S. K. Sinha, “Power-law correlations and finite-size effects in silica particle aggregates studied by small-angle neutron scattering,” Phys. Rev. B, vol. 33, pp. 269–275, Jan 1986. [Online]. Available: https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevB.33.269
[37] S.-H. Chen and J. Teixeira, “Structure and fractal dimension of proteindetergent complexes,” Phys. Rev. Lett., vol. 57, pp. 2583–2586, Nov 1986. [Online]. Available: https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevLett.57.2583
[38] A. Guinier and G. Fournet, Small-angle scattering of X-rays, ser. Structure of matter series. Wiley, 1955.
[39] Z. Zhou, Z. Zhao, H. Zhang, Z. Wang, X. Chen, R. Wang, Z. Chen, and J. Gao, “Interplay between longitudinal and transverse contrasts in fe3o4 nanoplates with (111) exposed surfaces,” ACS Nano, vol. 8, no. 8, pp. 7976–7985, 2014, pMID: 25093532. [Online]. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nn5038652
[40] H. Yang, T. Ogawa, D. Hasegawa, and M. Takahashi, “Synthesis and magnetic properties of monodisperse magnetite nanocubes,” Journal of Applied Physics, vol. 103, no. 7, p. 07D526, 2008. [Online]. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.2833820
[41] D. F. Coral and J. Mera, “Una guía para el estudio de nanopartículas magnéticas de óxidos de hierro con aplicaciones biomédicas. Parte I,” Ingeniería y Ciencia - ing.cienc., vol. 13, no. 25, pp. 229–249, 2017.
[42] R. Rosensweig, “Heating magnetic fluid with alternating magnetic field,” Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, vol. 252, pp. 370 – 374, 2002, proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Magnetic Fluids. [Online]. Available: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/ pii/S0304885302007060
[43] F. Tournus and E. Bonet, “Magnetic susceptibility curves of a nanoparticle assembly, i: Theoretical model and analytical expressions for a single magnetic anisotropy energy,” Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, vol. 323, no. 9, pp. 1109 – 1117, 2011. [Online]. Available: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304885310008401
[44] F. Tournus and A. Tamion, “Magnetic susceptibility curves of a nanoparticle assembly ii. simulation and analysis of zfc/fc curves in the case of a magnetic anisotropy energy distribution,” Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, vol. 323, no. 9, pp. 1118 – 1127, 2011. [Online]. Available: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304885310008413
[45] D. Serantes, K. Simeonidis, M. Angelakeris, O. Chubykalo-Fesenko, M. Marciello, M. d. P. Morales, D. Baldomir, and C. Martinez-Boubeta, “Multiplying magnetic hyperthermia response by nanoparticle assembling,” The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, vol. 118, no. 11, pp. 5927–5934, 2014. [Online]. Available: http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jp410717m